Emerald Ash Borer FAQ
Learn about the Emerald Ash Borer in Ontario, an invasive species that is killing ash trees and spreading across Canada.
Q: What is the Emerald Ash Borer?
A: An insect which was imported from Asia in the late 1990s in the Windsor area.
Q: How does the Emerald Ash Borer affect the tree?
A: Eggs are laid on the trunk in the summer. When they hatch the larvae bore into the bark and live by feeding on the tissue under the bark and creating tunnels. These tunnels disrupt the flow of nutrients.
Q: Which trees are affected by the Emerald Ash Borer?
A: Native and imported species of Ash.
Q: What will happen to an infested tree?
A: If no treatment is implemented, an infested tree will die in one to three years.
Q: What signs should I look for in my trees?
A: Thinning leaves at the top of the tree, cracking in the bark on the trunk, and new shoots and buds appearing on the lower trunk.
Q: What is the prevention or treatment?
A: There are natural and chemical tree trunk injection treatments for use before infestation. If Emerald Ash Borer is found in your Ash tree, the tree will most likely have to be removed. We can provide some suggestions based on your tree assessment.
Q: Where is the Emerald Ash Borer active?
A: Peterborough west to Windsor and in pockets across Ontario and Quebec.
Q: Where is the Emerald Ash Borer’s regulated area in Ontario?
A: The regulated area can be seen below, according to the Canadian Food Inspection Agency:
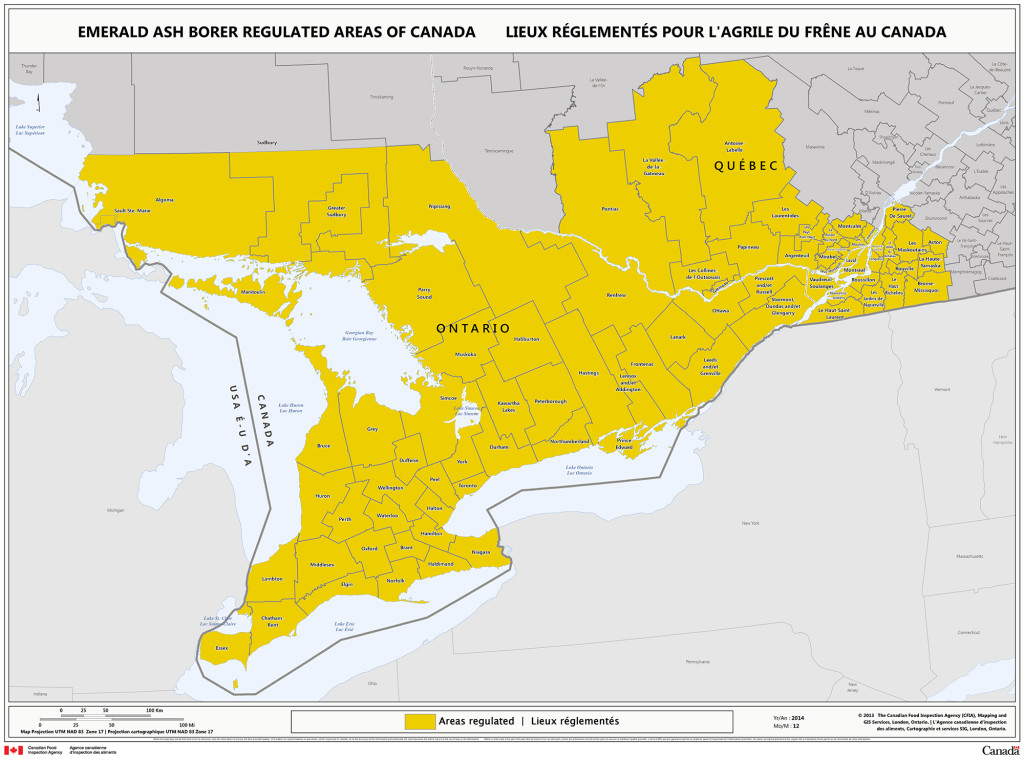
If you believe your tree could be infested with Emerald Ash Borer, or if you have any inquiries, please contact us!
